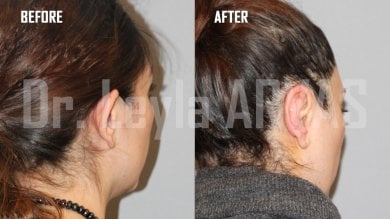
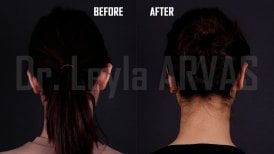
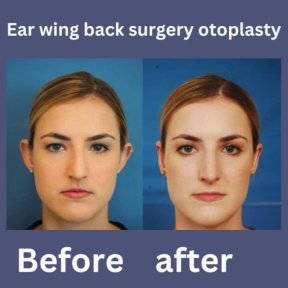
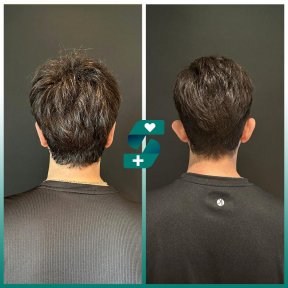
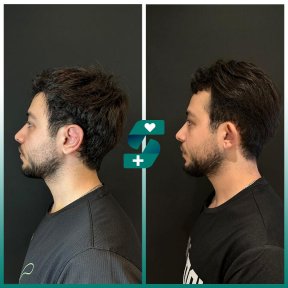
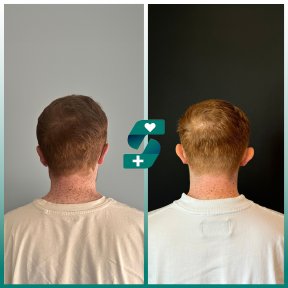
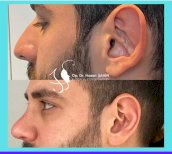
What is otoplasty?
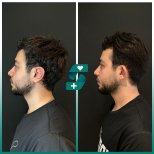
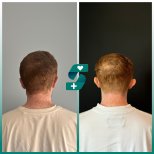
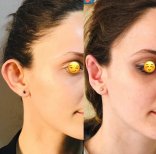
Otoplasty or ear surgery is a cosmetic surgery to improve the size and shape of the ears and eliminating lop ears. The operation minimizes post-traumatic or congenital ear defects. The method of otoplasty depends on the type of deformity.
What are ear surgery types?
Depending on the goals this intervention has to achieve, specialists distinguish two types of otoplasty:
- aesthetic — performed to eliminate any cosmetic defects (lop ears, too large auricles or their asymmetry)
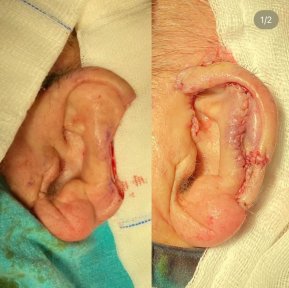
- reconstructive — required in case of the auricle congenital deformities or their complete absence.
What are the indications for otoplasty?
Ear surgery helps correct:
- lop ears
- the auricles congenital deformities
- cup ear deformity
- torn earlobe repair
- missing auricle.
Any congenital malformation of the auricles causes the vast majority of visits to plastic surgeons.
What are the contraindications to the surgery?
Contraindications to otoplasty are almost the same as to any other plastic surgery but include some specific ones. Among them are:
- bleeding disorders
- infectious diseases
- exacerbation of any chronic diseases
- inflammatory diseases of the ear, nose and throat
- external ear inflammatory diseases
- diabetes
- menstruation
- pregnancy
- oncological diseases
- immunodeficiencies.
What is the preparation period before ear surgery?
Before performing ear surgery, the primary examination is required — blood tests (general, for HIV, RW, hepatitis B, and C), bleeding time test, chest X-ray, and ECG (electrocardiogram).
2 weeks before the plastic ear surgery, the doctor advises refusing medication intake that can affect blood coagulation.
Smokers are advised to quit smoking at least 4 weeks before having plastic surgery (or at least significantly reduce the number of cigarettes smoked).
It would be best if you also stopped drinking alcohol at this time (this complicates the postoperative period).
The day before the operation, you need to have a fast day, and on the day of otoplasty — refuse food entirely.
More about the preparation here.
What are the steps of the operation?
The ear surgery is an outpatient procedure and takes from 30 minutes to 2 hours. The intervention process is divided into seven steps:
- marking of tissues to be excised
- local anesthesia
- removal of excess skin in the fold of the auricle
- replacement and/or removal of cartilage fragments
- fixation of cartilage in a new position
- cosmetic skin suturing
- compression bandage.
In-hospital stay is not required. A patient can come back home right after the surgery.
How long is the recovery period after otoplasty?
Otoplasty is a relatively simple operation, and the patient returns home right after the procedure. During 3-7 days, the patient wears a fixing bandage to avoid auricle injuries, especially during sleep. In some cases, doctors recommend wearing a bandage at night for 3 weeks.
Sometimes the patient feels some pain after otoplasty. In such cases, the doctor may prescribe painkillers. Also, antibiotics are often prescribed as a preventive measure to prevent the occurrence of complications such as infection and inflammatory processes.
If non-absorbable sutures were used during the surgery, they are usually removed after 2 weeks.
There are some restrictions on physical activity. Doctors advise significantly limiting it for at least one month after ear surgery.
Some patients have questions regarding the possible impact of otoplasty on hearing. This operation does not affect hearing.
The final evaluation of the ear surgery result is carried out by the doctor only in 6 months.
Read more here.
What are the possible complications after ear surgery?
Otoplasty is not a difficult surgery, but it still an intervention so that it may lead to some complications:
- bruises and hematomas (especially in smoking patients; last approximately 1-2 weeks)
- inflammatory (usually in people with the weakened immune system)
- hypertrophic scars (commonly are caused by an individual skin tendency to scarring).